Contents
close all
clear
startup
startup
current_dir = pwd;
addpath([current_dir,'/mbin']);
cd results
Define general options for constraints
constraint.options_dyk.maxIt=20;
constraint.options_dyk.minIt=3;
constraint.options_dyk.evol_rel_tol=1e-5;
constraint.options_dyk.tol=1e-2;
constraint.options_dyk.feas_tol=1e-1;
constraint.options_dyk.log_feas_error=0;
constraint.options_dyk.log_vec=0;
constraint.ADMM_options.maxit=800;
constraint.ADMM_options.evol_rel_tol=1e-6;
constraint.ADMM_options.rho=1e2;
constraint.ADMM_options.adjust_rho=1;
constraint.ADMM_options.test_feasibility=0;
constraint.ADMM_options.feas_tol=1e-2;
optimization options
options.maxIter = 20;
options.memory = 5;
options.testOpt = 0;
options.progTol=1e-14;
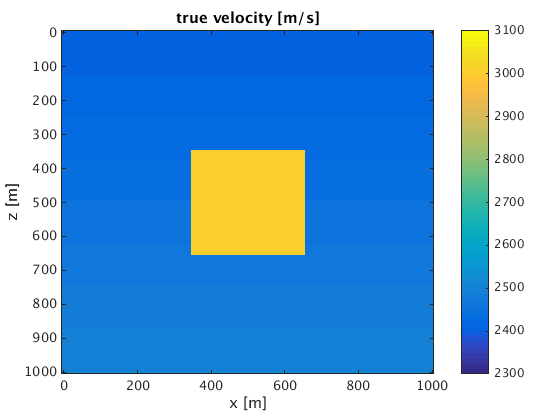
define velocity model
z = 0:10:1000;
x = 0:10:1000;
[o,d,n] = grid2odn(z,x);
[zz,xx] = ndgrid(z,x);
v0 = linspace(2400,2500,length(z))'*ones(1,length(x));
v = v0;
center_x = round(length(x)/2); center_z = round(length(z)/2);
v(center_z-15:center_z+15,center_x-15:center_x+15)=2500+.2*2500;
vpmin=min(v(:))-100;
vpmax=max(v(:))+100;
figure;imagesc(x,z,v,[vpmin vpmax]);xlabel('x [m]');ylabel('z [m]');title('true velocity [m/s]');colorbar;
set up the experiment: sources, receivers frequencies, source function
model_t.o = o;
model_t.d = d;
model_t.n = n;
model_t.freq = linspace(5,15,6); nfreq = length(model_t.freq);
model_t.f0 = 15;
model_t.t0 = 0;
model_t.zsrc = 0:100:1000; nsrc = length(model_t.zsrc);
model_t.xsrc = 50;
model_t.zrec = 0:10:1000; nrec = length(model_t.zrec);
model_t.xrec = 950;
model_t.n(3)=1;
model_t.d(3)=1;
model_t.o(3)=0;
Q = speye(nsrc);
m = 1e6./(v(:)).^2;
m0 = 1e6./v0(:).^2;
params=[];
if isfield(params,'pdefunopts')==0
params.pdefunopts = PDEopts2D();
end
if isfield(params,'lsopts')==0
solve_opts = LinSolveOpts();
solve_opts.solver = LinSolveOpts.SOLVE_LU;
params.lsopts = solve_opts;
end
create synthetic 'observed' data
D_t = F(m,Q,model_t,params);
create function handle for misfit
params.wri = false;
params.dist_mode = 'freq';
fh = misfit_setup(Q,D_t,model_t,params);
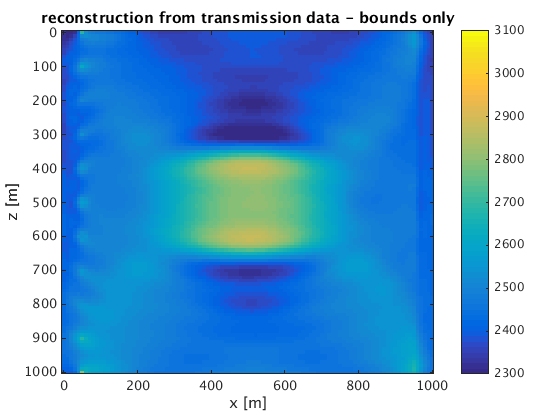
use SPG with only bound constraints
constraint.v_max = vpmax;
constraint.v_min = vpmin;
constraint.use_bounds = 1;
constraint.use_min_smooth = 0;
constraint.use_nuclear = 0;
constraint.use_rank = 0;
constraint.use_TV = 0;
constraint.use_cardinality = 0;
constraint.use_TD_bounds = 0;
constraint.use_cvxbody = 0;
params.freq_index=[1:length(model_t.freq)];
P = setup_constraints_freq_FWI_2D(constraint,model_t,model_t,params,m0,1);
funProj =@(input) P{1}(input);
[mn_t,fsave,funEvals,projects,iter_save] = minConf_SPG(fh,m0,funProj,options);
mn_t=1e3./sqrt(mn_t);
figure;imagesc(x,z,reshape(real(mn_t),n),[vpmin vpmax]);xlabel('x [m]');ylabel('z [m]');title('reconstruction from transmission data - bounds only');
colorbar
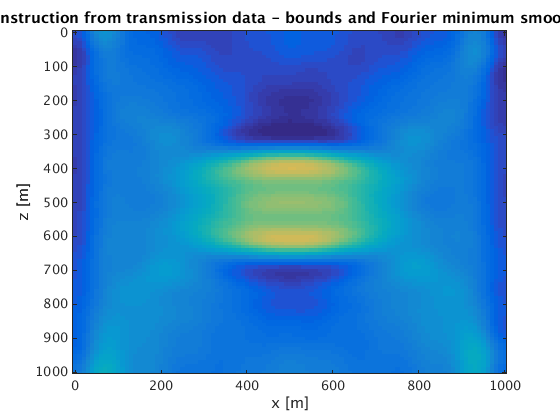
solve transmission experiment - bounds and Fourier based minimum smoothness
constraint.v_max = vpmax;
constraint.v_min = vpmin;
constraint.smoothpars = [3, 3, 1];
constraint.use_bounds = 1;
constraint.use_min_smooth = 1;
constraint.use_nuclear = 0;
constraint.use_rank = 0;
constraint.use_TV = 0;
constraint.use_cardinality = 0;
constraint.use_TD_bounds = 0;
constraint.use_cvxbody = 0;
params.freq_index=[1:length(model_t.freq)];
P = setup_constraints_freq_FWI_2D(constraint,model_t,model_t,params,m0,1);
funProj = @(input) Dykstra_prox_parallel(input,P,constraint.options_dyk);
[mn_t,fsave,funEvals,projects,iter_save] = minConf_SPG(fh,m0,funProj,options);
mn_t=1e3./sqrt(mn_t);
figure;imagesc(x,z,reshape(mn_t,n),[vpmin vpmax]);xlabel('x [m]');ylabel('z [m]');title('reconstruction from transmission data - bounds and Fourier minimum smoothness');
transmission experiment - Bound constraints and rank
constraint.v_max = vpmax;
constraint.v_min = vpmin;
constraint.r_initial = 2;
constraint.r_increment = 0;
constraint.use_bounds = 1;
constraint.use_min_smooth = 0;
constraint.use_nuclear = 0;
constraint.use_rank = 1;
constraint.use_TV = 0;
constraint.use_cardinality = 0;
constraint.use_TD_bounds = 0;
constraint.use_cvxbody = 0;
params.freq_index=[1:length(model_t.freq)];
P = setup_constraints_freq_FWI_2D(constraint,model_t,model_t,params,m0,1);
funProj = @(input) Dykstra_prox_parallel(input,P,constraint.options_dyk);
[mn_t,fsave,funEvals,projects,iter_save] = minConf_SPG(fh,m0,funProj,options);
mn_t=1e3./sqrt(mn_t);
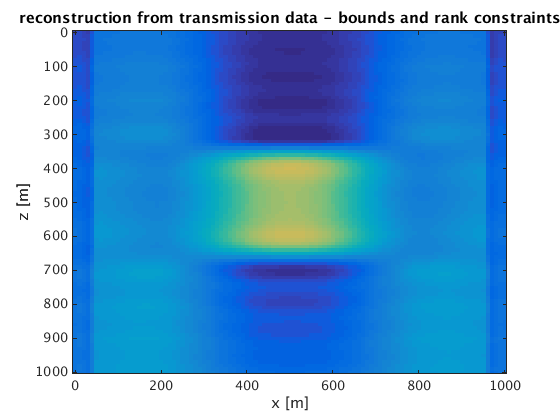
figure;imagesc(x,z,reshape(mn_t,n),[vpmin vpmax]);xlabel('x [m]');ylabel('z [m]');title('reconstruction from transmission data - bounds and rank constraints');
transmission experiment - Bound constraints and TV
constraint.v_max = vpmax;
constraint.v_min = vpmin;
constraint.TV_initial = 3;
constraint.TV_increment = 1;
constraint.TV_proj = 'admm';
constraint.TV_units = 's^2/m^2';
constraint.use_bounds = 1;
constraint.use_min_smooth = 0;
constraint.use_nuclear = 0;
constraint.use_rank = 0;
constraint.use_TV = 1;
constraint.use_cardinality = 0;
constraint.use_TD_bounds = 0;
constraint.use_cvxbody = 0;
params.freq_index=[1:length(model_t.freq)];
P = setup_constraints_freq_FWI_2D(constraint,model_t,model_t,params,m0,1);
funProj = @(input) Dykstra_prox_parallel(input,P,constraint.options_dyk);
[mn_t,fsave,funEvals,projects,iter_save] = minConf_SPG(fh,m0,funProj,options);
mn_t=1e3./sqrt(mn_t);
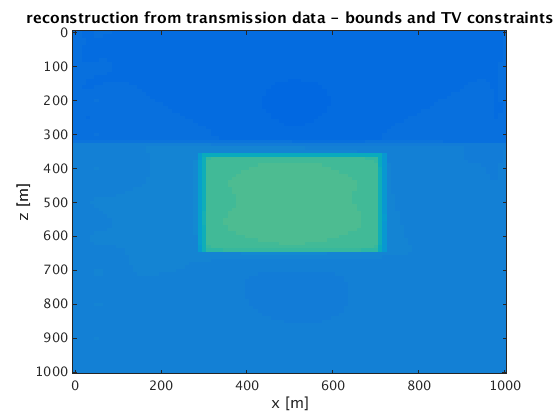
figure;imagesc(x,z,reshape(mn_t,n),[vpmin vpmax]);xlabel('x [m]');ylabel('z [m]');title('reconstruction from transmission data - bounds and TV constraints');
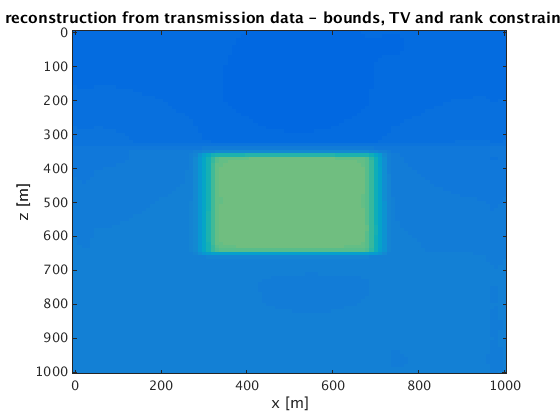
transmission experiment - Bound constraints and TV and rank
constraint.v_max = vpmax;
constraint.v_min = vpmin;
constraint.TV_initial = 4;
constraint.TV_increment = 1;
constraint.TV_proj = 'admm';
constraint.TV_units = 'm/s';
constraint.r_initial = 2;
constraint.r_increment = 0;
constraint.use_bounds = 1;
constraint.use_min_smooth = 0;
constraint.use_nuclear = 0;
constraint.use_rank = 1;
constraint.use_TV = 1;
constraint.use_cardinality = 0;
constraint.use_TD_bounds = 0;
constraint.use_cvxbody = 0;
params.freq_index=[1:length(model_t.freq)];
P = setup_constraints_freq_FWI_2D(constraint,model_t,model_t,params,m0,1);
funProj = @(input) Dykstra_prox_parallel(input,P,constraint.options_dyk);
[mn_t,fsave,funEvals,projects,iter_save] = minConf_SPG(fh,m0,funProj,options);
mn_t=1e3./sqrt(mn_t);
figure;imagesc(x,z,reshape(mn_t,n),[vpmin vpmax]);xlabel('x [m]');ylabel('z [m]');title('reconstruction from transmission data - bounds, TV and rank constraints');