Sparsity-promoting denoising: examples and results
Author: Haneet Wason (hwason@eos.ubc.ca)
Date: December, 2015
Contents
% Set paths curdir = pwd; basedir = curdir(1:end-4); datadir = [basedir '/data']; resultsdir = [basedir '/results']; % Load input data and previously computed results % NOTE: DG => Dynamic geometry; SG => Static geometry D_input_DG = rsf_read_all([datadir '/FreqInd30_DG.rsf']); Dden_DG_WRAP = rsf_read_all([resultsdir '/FreqInd30_DG_WRAPcurv_denoised.rsf']); Dden_DG_ME = rsf_read_all([resultsdir '/FreqInd30_DG_MEcurv_denoised.rsf']); Dden_SG_WRAP = rsf_read_all([resultsdir '/FreqInd30_SG_WRAPcurv_denoised.rsf']); Dden_SG_ME = rsf_read_all([resultsdir '/FreqInd30_SG_MEcurv_denoised.rsf']); % Plotting parameters cax = 1e-7; cmap = 'seiscol'; % x-axis label for plots xlab = 'Shot (#)'; % y-axis label for plots ylab_DG = 'Channel (#)'; ylab_SG = 'Receiver (#)';
Dynamic geometry (DG) vs. Static geometry (SG)
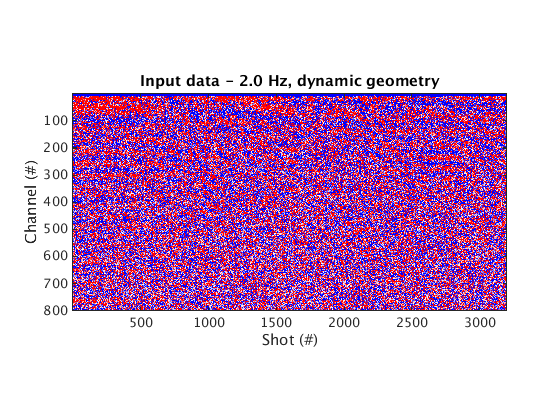
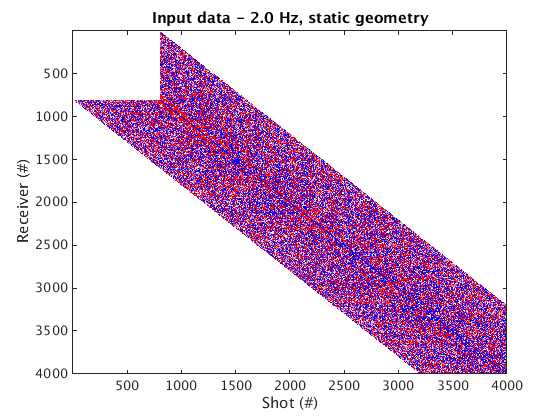
Input data is a frequency slice extracted from a seismic data cube simulated from a towed-streamer (moving receivers, DG) geometry
% Dynamic geometry - moving receivers figure; imagesc(real(D_input_DG), [-1 1]*cax); colormap(cmap); title('Input data - 2.0 Hz, dynamic geometry'); set(gca, 'plotboxaspectratio', [2 1 2]); xlabel(xlab); ylabel(ylab_DG); % Static geometry - fixed receivers % NOTE: the static geometry is useful for (frequency-domain) FWI algorithms that rely on fixed receivers D_input_SG = fdata2AcqGrid(D_input_DG, 1); figure; imagesc(real(D_input_SG), [-1 1]*cax); colormap(cmap); title('Input data - 2.0 Hz, static geometry'); xlabel(xlab); ylabel(ylab_SG);
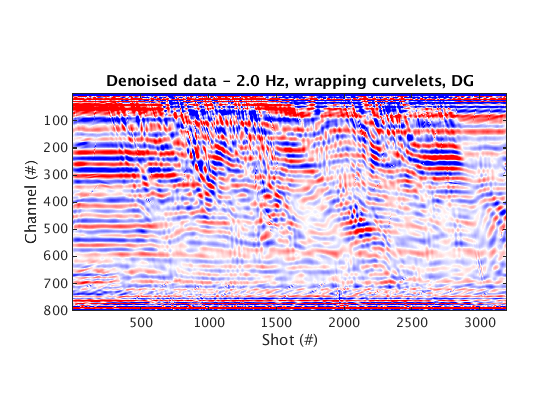
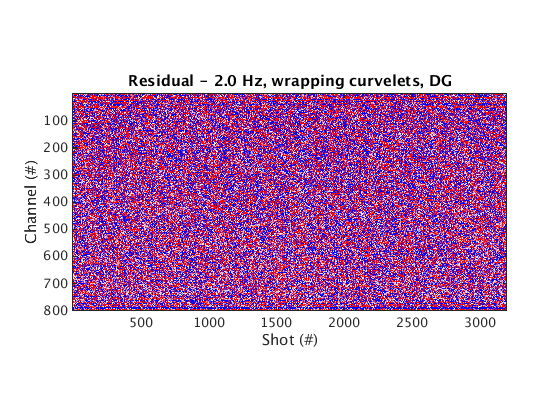
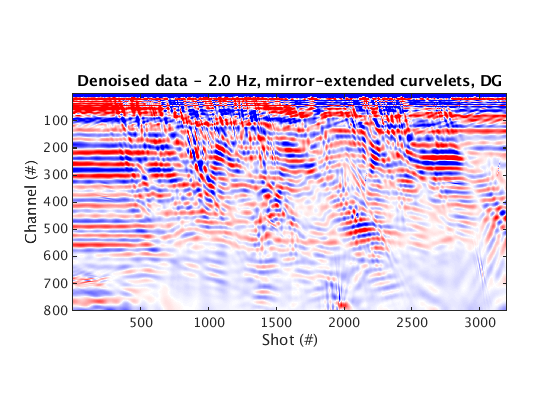
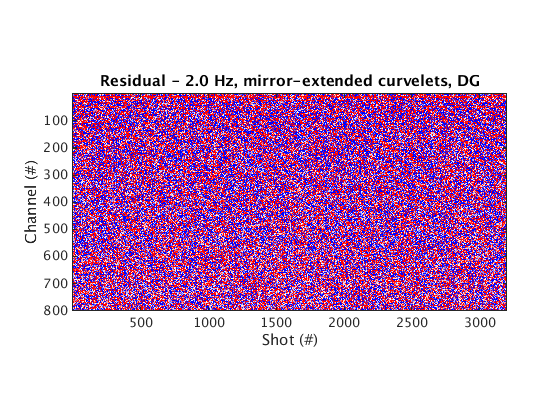
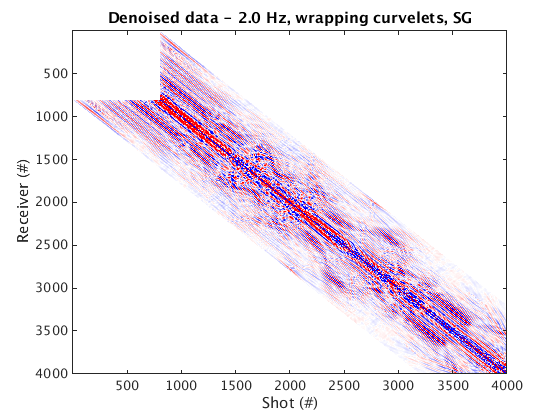
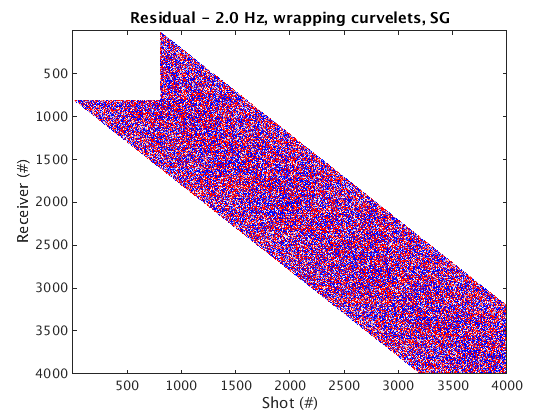
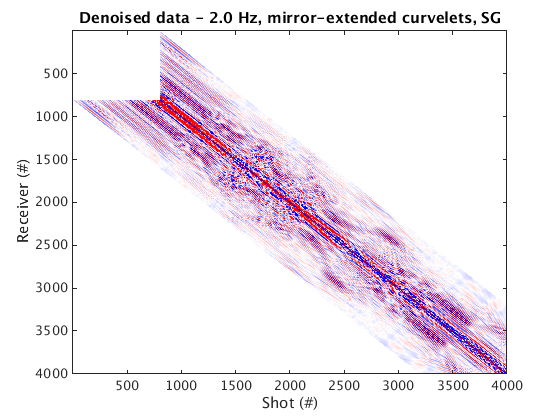
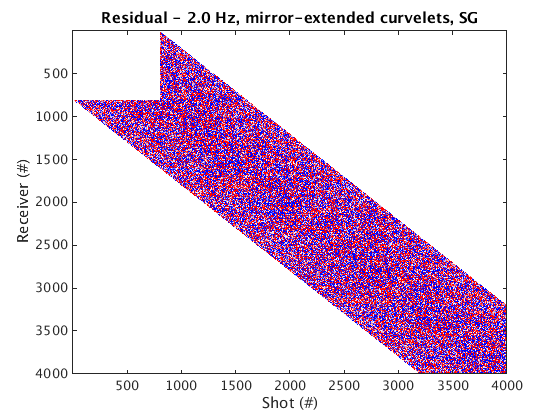
Denoised data and residual
% Dynamic geometry % Wrapping curvelets % NOTE: the lines that appear near the bottom edge of the denoised data are due to the wrap-around effect of wrapping curvelets figure; imagesc(real(Dden_DG_WRAP), [-1 1]*cax); colormap(cmap); title('Denoised data - 2.0 Hz, wrapping curvelets, DG'); set(gca, 'plotboxaspectratio', [2 1 2]); xlabel(xlab); ylabel(ylab_DG); figure; imagesc(real(D_input_DG - Dden_DG_WRAP), [-1 1]*cax); colormap(cmap); title('Residual - 2.0 Hz, wrapping curvelets, DG'); set(gca, 'plotboxaspectratio', [2 1 2]); xlabel(xlab); ylabel(ylab_DG); % Mirror-extended curvelets figure; imagesc(real(Dden_DG_ME), [-1 1]*cax); colormap(cmap); title('Denoised data - 2.0 Hz, mirror-extended curvelets, DG'); set(gca, 'plotboxaspectratio', [2 1 2]); xlabel(xlab); ylabel(ylab_DG); figure; imagesc(real(D_input_DG - Dden_DG_ME), [-1 1]*cax); colormap(cmap); title('Residual - 2.0 Hz, mirror-extended curvelets, DG'); set(gca, 'plotboxaspectratio', [2 1 2]); xlabel(xlab); ylabel(ylab_DG); % Static geometry % Wrapping curvelets Dden_SG_WRAP = fdata2AcqGrid(Dden_SG_WRAP, 1); figure; imagesc(real(Dden_SG_WRAP), [-1 1]*cax); colormap(cmap); title('Denoised data - 2.0 Hz, wrapping curvelets, SG'); xlabel(xlab); ylabel(ylab_SG); figure; imagesc(real(D_input_SG - Dden_SG_WRAP), [-1 1]*cax); colormap(cmap); title('Residual - 2.0 Hz, wrapping curvelets, SG'); xlabel(xlab); ylabel(ylab_SG); % Mirror-extended curvelets Dden_SG_ME = fdata2AcqGrid(Dden_SG_ME, 1); figure; imagesc(real(Dden_SG_ME), [-1 1]*cax); colormap(cmap); title('Denoised data - 2.0 Hz, mirror-extended curvelets, SG'); xlabel(xlab); ylabel(ylab_SG); figure; imagesc(real(D_input_SG - Dden_SG_ME), [-1 1]*cax); colormap(cmap); title('Residual - 2.0 Hz, mirror-extended curvelets, SG'); xlabel(xlab); ylabel(ylab_SG);