Sparsity promoting LSRTM with linearized Bregman
Example script for running least-squares RTM with sparsity promotion and source subsampling on the Marmousi model.
Author: Philipp Witte Date: February 2016
Contents
Set paths to result,data,model etc.
clear all; clc; rng('default') % Load software release functions % SLIM_APPS.tools.algorithms.TimeModeling addpath(genpath('~/SLIM-release-apps')); % paths and name of results and snapshots snapshotX = 'UpdateTest_X.mat'; snapshotZ = 'UpdateTest_Z.mat'; result = 'Result.mat'; params = 'Parameters.mat'; % pull data and model % if ~exist('../data/modelMarmousi.mat','file') % cd ../data/; ! scons; cd ../examples/; % end % Marmousi slowness^2 model [s^2/km^2] load modelMarmousi.mat % Load 2D data cube [ns x nrec x nsrc] % load ../data/linDataMarmousi.mat
Modeling parameters
Set up a structure that contains information about the velocity model and the source/receiver geometry of the input data.
% model parameters model.o = [0, 0, 0]; % Origin [m] model.n = [320, 800, 1]; % no. of grid points [z,x,y] model.d = [10, 10, 10]; % grid spacing [m] model.freesurface = 0; % data parameters model.f0 = 0.030; % peak frequency [MHz] model.T= 4000; % Recording length [ms] model.NyqT=0:4:model.T; % Shot record time axis [ms] % source/receiver position [m] model.xsrc = 25:25:(n(2)*d(2)); model.zsrc = 10*ones(size(model.xsrc)); model.ysrc = 0*ones(size(model.xsrc)); model.xrec = 5:10:n(2)*d(2)-5; model.zrec = 210; model.yrec = 0; % Code specific options model.save = 'RAM'; % save wavefields in memory model.type='full'; % acquisition geometry model.space_order=4; % Order of Laplacian % Domain decomposition model.ddcompx = 1; model.ddcompz = 1; model.ddcompy = 1;
LSRTM parameters
Define the number of iterations for the linearized Bregman method, as well as the L2 norm of the noise  , the thresholding value
, the thresholding value  and the number of sources per iteration. Furthermore, set up a structure that defines which preconditioners are used. All
preconditioners are disabled as default and can be enabled by setting them to '1'.
and the number of sources per iteration. Furthermore, set up a structure that defines which preconditioners are used. All
preconditioners are disabled as default and can be enabled by setting them to '1'.
% LSRTM options options.iterations = 40; options.lambda = []; options.sigma = 0; options.numShots = 8; % No. of shots per Bregman iteration options.snapshotX = snapshotX; options.snapshotZ = snapshotZ; % Preconditioners precon.modelDepth = 1; precon.modelTopmute = 1; precon.dataScaling = 1; precon.dataTopmute = 1;
Setup grid and modeling options
% Calculate optimal grid size and time step [m,model,dmTrue]=Setup_CFL(m,model,dm); % Source wavelet q=sp_RickerWavelet(model.f0,1/model.f0,model.dt,model.T);
CFL conditions gives dt = 0.57736ms and d = 5 5 5 m Velocity interpolated on new grid
Call algorithm and save results
Runtime per iteration (one demigration and one migration) for this example was ~20 minutes.
% [dm,info] = linbregLSRTM(dData,model,m0,q,precon,options); % save(result,'dm','info'); % save(params,'model');
Plot results
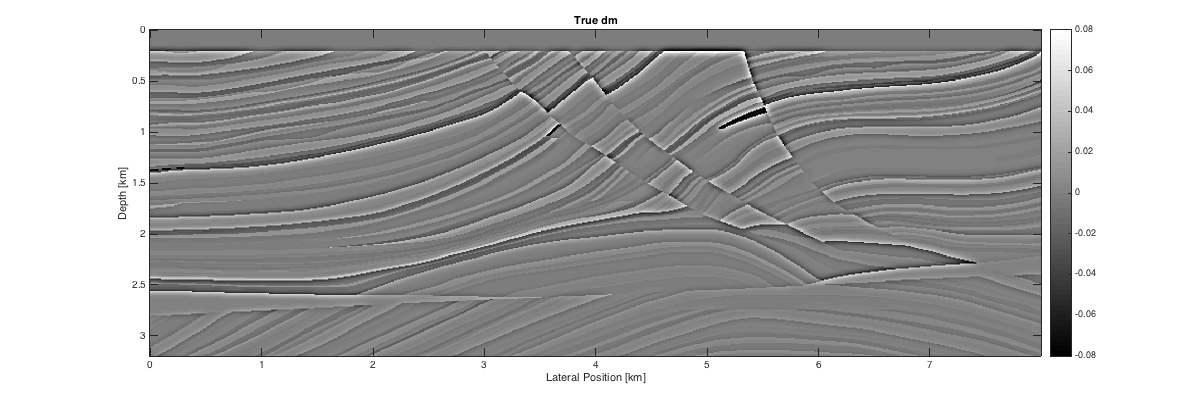
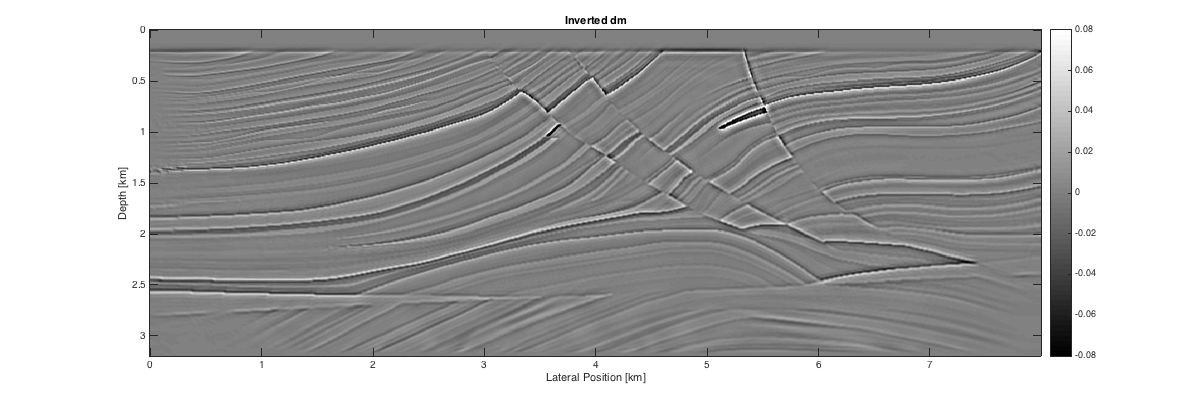
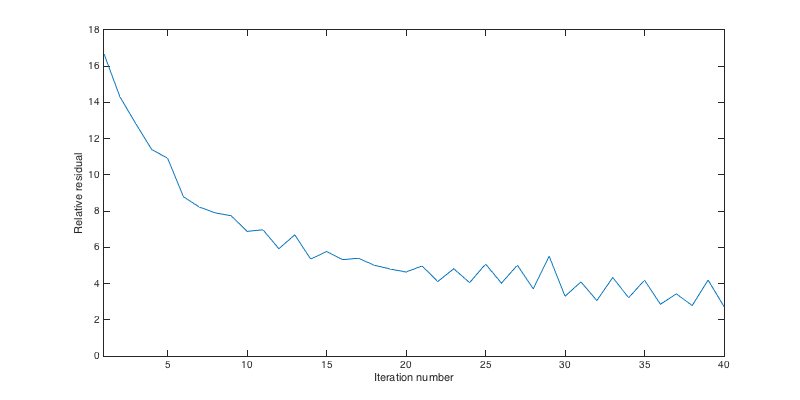
load Result.mat load Parameters.mat x = linspace(0,7.995,model.n(2)); z = linspace(0,3.195,model.n(1)); % true image figure('Position',[400,400,1200,400]); imagesc(x,z,reshape(-dmTrue,model.n)); xlabel('Lateral Position [km]'); ylabel('Depth [km]'); colormap gray; caxis([-1 1]*8e-2); colorbar title('True dm'); % lsrtm image figure('Position',[400,400,1200,400]); imagesc(x,z,dm); xlabel('Lateral Position [km]'); ylabel('Depth [km]'); colormap gray; caxis([-1 1]*8e-2); colorbar title('Inverted dm'); figure('Position',[400,400,800,400]); plot(info.residual) xlabel('Iteration number'); ylabel('Relative residual'); axis([1 40 0 18]);